
As the name suggests, in an n Channel MOSFET, the channel is made up of n type of current carriers i.e. This minimum voltage is called threshold voltage of a MOSFET and the current flow is due to the formation of a channel from drain to source in the substrate of the MOSFET. When a certain minimum voltage is reached, the resistance drops and the MOSFET starts conducting and the current starts to flow from drain to source. I grounded the source now and started increasing the gate voltage. When no voltage is applied in the gate terminal, two back to back diodes exists between the substrate and drain and source region causing the path between drain and source to have a resistance in the order of 10 to the power 12 ohms. The arrow direction in this symbol depicts the conventional direction of electron flow inside a MOSFET, which is opposite to that of the current flowĪ Bipolar Junction Transistor or a BJT is a current controlled device, that means the amount of current flow in its base terminal determines the current that will flow through the transistor, but we know that there is no role of current in MOSFETs gate terminal and collectively we can say that it is a voltage controlled device not because gate current is always zero but because of its structure which I’ll not explain in this Instructable because of its complicacy. Placing another line on the gate makes sense while relating them to the JFETs, indicating the gate has been insulated. The symbol for MOSFETs can be seen in the picture attached. These are also very important while studying on a professional level. This capacitance is called gate capacitance and can easily destroy your circuit if not taken in to account. In the gate region, you can see that a parallel plate capacitor like structure is formed and it actually introduces a considerable capacitance to the gate terminal. A layer of a good conductor like aluminium is grown additionally above all the three regions, and then contacts are made.

This is the reason why it’s also called Insulated Gate Field Effect Transistor (IGFET). This increases the gate resistance in the scale of ten to the power ten ohms and we assume that in a MOSFET gate current Ig is always zero. SiO2 is a very good dielectric, or you can say insulator. This is the reason it is named Metallic Oxide Semiconductor Field effect Transistor. Before making the contacts for the gate terminal a layer of Silicon Dioxide is grown above the substrate.
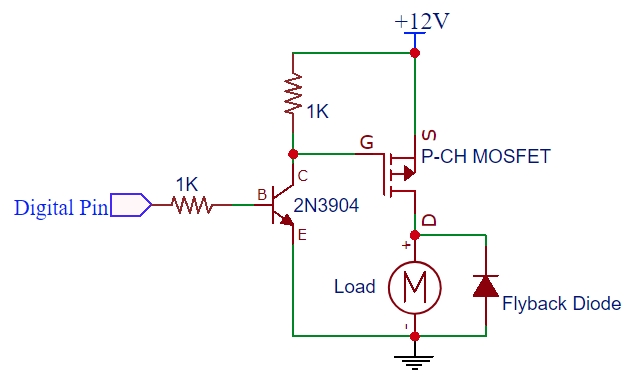
After this comes the MOSFET, having a major difference in the gate terminal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
